The world wide web is constantly evolving, and it is important to know the history and how it has improved over the years. In this article we will discuss the different iterations of the web from Web 1.0 to Web 5.0 and what the future hold.
As we step into the world of artificial intelligence and technological advancements growing at an exponential rate, we should look back at the growth of the World Wide Web and how it has evolved over the years.
In this article we will discuss all the aspects of the World Wide Web, from Web 1.0 to Web 5.0 and where it stands today.
Overview of Web Evolution From Web 1.0 to Web 5.0
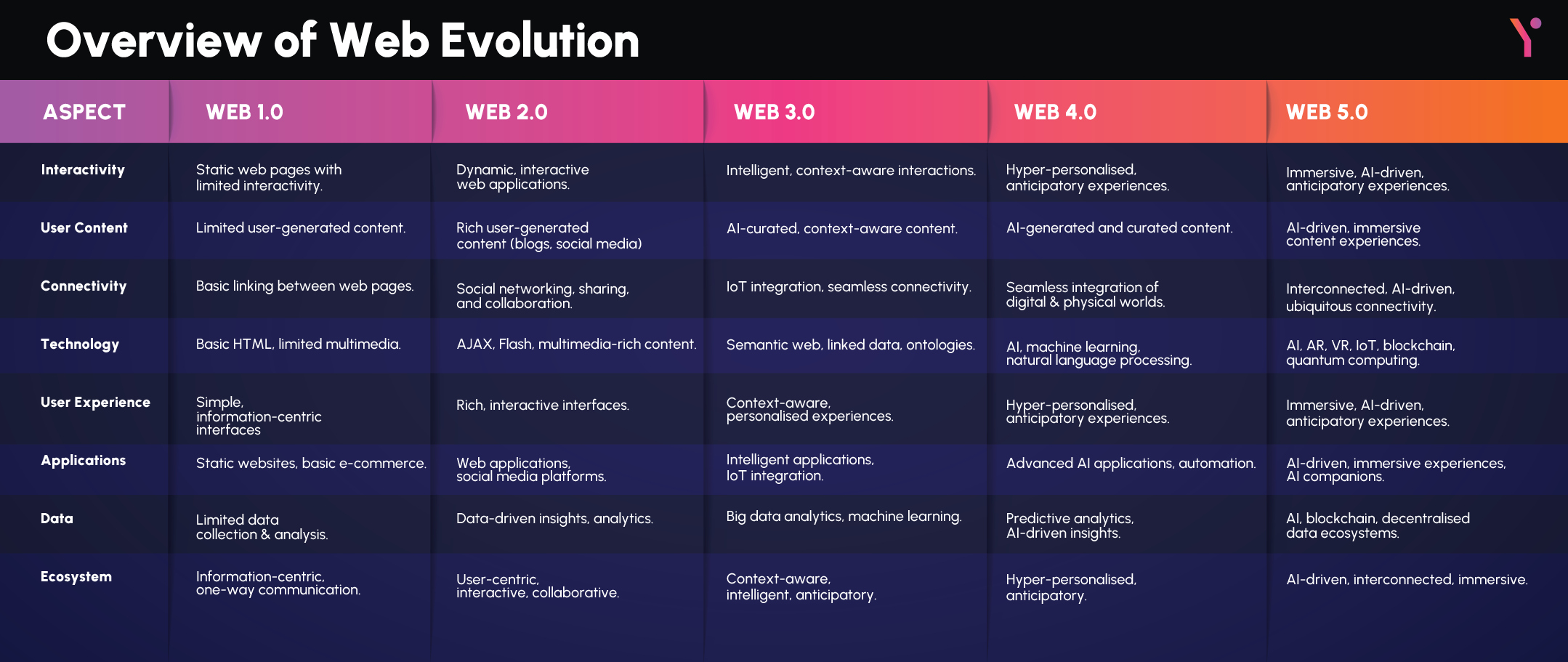
The internet came into inception in 1989 when a scientist named Tim Berners-Lee saw the demand of information sharing between institutions and across the world and wanted to create a solution that would automate this process. Fast forward 35 years and we are currently in an era where the internet allows anyone to access information within seconds and even recruit the help of AI online to help us with everyday tasks. This table will discuss all the aspects of Web 1,0 to Web 5.0
It is impressive to see the growth the internet has achieved in just over 3 decades. Let’s discuss each iteration of the world wide web and how it impacted people on a global scale.
Web 1.0: The Static Web
Web 1.0, also known as the Static Web, refers to the early days of the World Wide Web when websites were primarily static and information was presented in a one-way manner. This is the earliest form of the internet that was common used in the early 90s, during the days of dial-up connections.
Web 1.0 revolutionised communication by making information accessible to a global audience. It empowered individuals to access knowledge, news, and resources from anywhere with an internet connection. However, Web 1.0 had some limitations when it came to interaction, and users were passive consumers of content rather than active participants in the web experience. It was only until the next iteration that the social web came into being.
Web 2.0: The Social Web
Web 2.0 marked the shift from static websites to dynamic, interactive platforms that enabled user-generated content, social networking, and collaboration.
The Social Web transformed how people interacted online, fostering communities, connecting individuals worldwide, and facilitating communication in real-time. It gave rise to social media platforms, blogs, wikis, and other user-driven content sites, democratising the creation and sharing of information. Web 2.0 empowered users to express themselves, share their thoughts and experiences, and participate in online discussions.
Web 3.0: The Semantic Web
Web 3.0, also known as the Semantic Web, refers to the vision of a more intelligent, context-aware web that understands the meaning of information and can provide personalised, relevant content and services. This is when web development company and WordPress web design services started to emerge.
While the full realisation of the Semantic Web is still evolving, advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing have enabled significant progress. Web 3.0 has the potential to revolutionise information retrieval, making it easier for users to find relevant content, discover new resources, and navigate the vastness of the web. It promises more efficient search engines, personalised recommendations, and seamless integration of data from disparate sources.
It also gave a rise to custom website development and progressive web applications. People in this era were slowly understanding the need for a website for their business.
Web 4.0: The Intelligent Web
Web 4.0 envisions a web ecosystem powered by advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation, where data-driven insights and intelligent systems enhance user experiences and enable new capabilities.
The Intelligent Web represents the next evolution of digital transformation, where AI-driven applications, smart devices, and interconnected systems revolutionise various industries. It has the potential to transform how businesses operate, optimise processes, and deliver personalised experiences to customers. Web 4.0 is driving innovation in areas such as healthcare, finance, transportation, and education, enabling smarter decision-making, predictive analytics, and autonomous systems.
Web 5.0: The Immersive Web
Web 5.0, a speculative concept, represents a future stage of web development characterised by immersive experiences, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and the convergence of digital and physical realities. The most recent advancement of this aspect can be seen with the new Apple Vision Pro, which takes AR and VR to the next level in everyday life
While Web 5.0 is still in the realm of speculation, the concept highlights the growing importance of immersive technologies in shaping the future of the web. AR and VR have the potential to revolutionise how people interact with digital content, transforming entertainment, education, training, and more. The Immersive Web could redefine user experiences, blurring the lines between the virtual and physical worlds, and opening up new possibilities for creativity, exploration, and collaboration.
Impact of The Web on Industries
Over the years, the world wide web and its evolution has allowed several industries to improve their processes and enhance their growth. Following are some of the improvements that businesses have enjoyed in different industries thanks to the evolution of the world wide web.
Automotive
- Increased Connectivity: The web has transformed the automotive industry by enabling connectivity features in vehicles, such as GPS navigation, real-time traffic updates, and vehicle diagnostics.
- Online Sales and Services: Automakers and dealerships leverage the web to market and sell vehicles online, offer virtual showrooms, and provide digital services like scheduling maintenance appointments and ordering parts.
E-commerce
- Global Reach: The web has revolutionised the retail sector by providing a platform for online stores to reach customers worldwide, breaking down geographical barriers and expanding market reach.
- Digital Payments: E-commerce relies heavily on web-based payment systems, enabling secure and convenient transactions for customers and businesses alike.
- Personalised Shopping Experience: Advanced analytics and recommendation engines on e-commerce websites use web data to offer personalised product recommendations, enhancing the shopping experience and increasing sales.
Finance
- Online Banking: The web has transformed the banking industry by enabling customers to access banking services remotely, including account management, fund transfers, bill payments, and loan applications.
- Trading Platforms: The rise of web-based trading platforms has democratised investment, allowing individuals to buy and sell stocks, bonds, and other securities online.
- Financial Education: The web offers a wealth of resources for financial education, including articles, videos, tutorials, and interactive tools, empowering individuals to make informed financial decisions.
Healthcare
- Telemedicine: The web has facilitated the growth of telemedicine, enabling patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely, access medical information, and schedule appointments online.
- Health Information: Patients can research medical conditions, treatments, and medications online, empowering them to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Web-based EHR systems allow healthcare providers to securely store, access, and share patient health records, improving coordination of care and patient outcomes.
Retail
- Online Shopping: The web has transformed the retail industry by enabling consumers to shop for a wide range of products and services online, 24/7, from the comfort of their homes.
- Omnichannel Retailing: Retailers leverage the web to offer seamless shopping experiences across multiple channels, including websites, mobile apps, social media, and brick-and-mortar stores.
- Customer Engagement: Web-based tools such as email marketing, social media, and personalised recommendations help retailers engage with customers, build brand loyalty, and drive sales.
Real Estate
- Property Listings: Real estate websites allow buyers, sellers, and renters to search for properties, view photos and videos, and access information about neighborhoods, schools, and amenities.
- Virtual Tours: Web-based virtual tour technology enables prospective buyers to explore properties remotely, providing a more immersive and convenient homebuying experience.
- Property Management: Web-based platforms streamline property management tasks such as tenant screening, lease management, rent collection, and maintenance requests.
Education
- Online Learning: The web has revolutionised education by providing access to online courses, virtual classrooms, and educational resources, allowing students to learn anytime, anywhere.
- Distance Learning: Web-based platforms facilitate distance learning programs, enabling students to earn degrees and certifications remotely, without the need to attend traditional brick-and-mortar institutions.
- Collaboration and Engagement: Web-based tools such as video conferencing, discussion forums, and interactive learning materials enhance collaboration and engagement among students and educators.
Entertainment
- Streaming Services: The web has transformed the entertainment industry by enabling the delivery of streaming media content, including movies, TV shows, music, and games, directly to consumers’ devices.
- Social Media: Web-based social media platforms provide a platform for users to connect, share content, and engage with friends, family, and communities, fostering new forms of entertainment and social interaction.
- User-Generated Content: The web has democratised content creation, allowing individuals to produce and distribute their own videos, music, podcasts, and other forms of entertainment, reaching global audiences without traditional gatekeepers.
Future Web Trends
During the covid period, we saw a surge in the use of the web, which is why the growth during and post-covid was exponential. According to Forbes, during the covid period, internet usage increased by 70%. This includes online transaction, streaming, and online classes.
The paradigm shift saw a number of advancements on the evolution of web and businesses took advantage of these advancements to improve their practices.
Fast forward to post-covid, businesses and individuals both understood the feasibility and utility of carrying on the online trend which in turn improved the growth curve of the world wide web.
We are quickly approaching an era where AR and VR are taking over. With the launch of the Apple Vision Pro and other AR capable devices, the next era of web is slowly becoming commonplace. We can anticipate that the future will consist of a completely AR and VR focused world with most processes happening in real-time.
Conclusion
The evolution of the world wide web has created opportunities for businesses all across the world. Experts are speculating the rise of Web 4.0 and Web 5.0 as a revolutionising era in the world wide web.
If you have a business and want to leverage the full potential of the world wide web, you need a technology partner that can help you every step of the way. This is where FuturByte comes into play. Contact us today and get services from a Joomla web developer, to website development and even a search engine marketing consultant. Get a free consultation on how you can improve your business processes with the help of the world wide web.
Frequently Asked Questions
The World Wide Web, commonly known as the web, is an information system that allows users to access and share documents and resources linked through hyperlinks. It is a crucial component of the internet and facilitates communication, collaboration, and information dissemination worldwide.
The World Wide Web was invented by Sir Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist, in 1989. He proposed the concept of a distributed information system while working at CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, and developed the first web browser and web server in 1990.
The World Wide Web has revolutionized communication, commerce, education, entertainment, and virtually every aspect of modern life. It has democratized access to information, connected people globally, facilitated e-commerce and online banking, transformed media consumption, and empowered individuals to create, share, and collaborate on a global scale.
The future of the World Wide Web is shaped by emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things (IoT), as well as ongoing challenges related to privacy, cybersecurity, digital inclusion, and ethical use of technology. It is essential to balance innovation with ethical, legal, and societal considerations to ensure a safe, inclusive, and sustainable web for future generations.
Have questions or feedback?
Get in touch with us and we‘l get back to you and help as soon as we can!




