This blog aims to describe everything you need to know about testing approaches: Black Box vs White Box testing. By understanding their key differences and how they work, you’ll be better equipped to choose the right testing method for your project and achieve optimal software quality.
Have you ever been frustrated by a website that crashes unexpectedly or an app that simply refuses to work the way it should? Software bugs like these are annoying, and, at times, they may be costly for businesses and users alike.
That’s where software testing comes in, playing a major role in ensuring the quality, functionality, and user satisfaction of any software we interact with.
Software development is one thing, but testing if it works fine is all one wants. Software testing helps track and determine any bugs and make sure the application runs smoothly.
There are two ways of testing: black box testing and white box testing. But knowing how they’re different is really important for testing software effectively. So, we’ll explore the difference between black box vs white box testing to help you understand when each one is best for custom website development.
What is Software Testing?
Software testing is the recurring process of evaluated by an app development company to identify any discrepancies between expected and actual results. It involves executing the software under controlled conditions and observing its behaviour to uncover defects or bugs. By rigorously testing software throughout its development lifecycle, developers may determine and rectify bugs, guaranteeing that the final product meets quality standards and user expectations.
When Do You Need Software Testing?
Software testing is indispensable at various stages of the development lifecycle, from the initial design phase to post-deployment maintenance. It is needed to:
- Make sure the software does what it’s supposed to.
- Find and fix any problems or errors.
- Check that it works on different devices and systems.
- Make sure it’s safe and easy to use.
- Improve the product so users are happy, and the software runs smoothly.
- Avoid situations like losing money or a bad reputation because of software issues.
Black Box Testing and Its Key Concepts
Black box testing is one way to test software. In black box testing, the focus remains on examining the functionality of an application without considering its internal structure or implementation details.
Testers focus on what the software does from the outside without looking at the code inside. It’s like you are testing a website’s clickable events without knowing how the buttons work inside. You just click and see if it responds the way you expect. This testing method checks if the software behaves correctly based on what users expect without needing to understand the technical stuff behind it.
Here are some key concepts associated with black box testing:
Functionality Testing
Black box testing primarily evaluates the functionality of the software by testing its inputs and outputs against specified requirements.
Test Cases
Test cases are implemented based on external specifications, user requirements, or system specifications without any knowledge of the internal code.
Boundary Value Analysis
This technique involves testing the application at the boundaries of input domains to find errors related to boundary conditions.
Equivalence Partitioning
Testers divide input data into partitions or classes and select representative values from each partition to design test cases.
Pros and Cons of Black Box Testing
| Pros | Cons |
Typical Use Cases and Examples
Black box testing is well-suited for:
- Testing user interfaces and interactions.
- Validating functional requirements.
- Assessing software usability and accessibility.
- Conducting system integration testing.
- Performing acceptance testing.
Example: Testing a web application’s login functionality without knowledge of its backend implementation.
White Box Testing and Its Key Concepts
The term “white box testing” refers to evaluating the software’s internal processes, logic, and structure.
White box testing requires you to access the source code and use expertise to design test cases that target specific paths, conditions, and statements within the code. You scrutinise every line to make sure it’s written correctly and working flawlessly from the inside out.
Here are some key concepts associated with white box testing:
Code Coverage
White box testing aims to achieve maximum code coverage by testing all possible paths through the code.
Path Testing
Test cases are designed to execute every possible path through the software, ensuring thorough testing of all logical branches.
Statement Coverage
This metric measures the percentage of executable statements that have been exercised by the test cases.
Branch Coverage
Branch coverage assesses the percentage of decision points in the code that have been tested.
Pros and Cons of White Box Testing
| Pros | Cons |
Typical Use Cases and Examples
White box testing is suitable for:
- Unit testing individual functions or modules.
- Validating algorithmic correctness.
- Identifying performance bottlenecks and optimisation opportunities.
- Ensuring code maintainability and readability.
- Detecting security vulnerabilities through code analysis.
Example: Testing a sorting algorithm’s implementation by examining its source code and designing test cases to cover all possible scenarios.
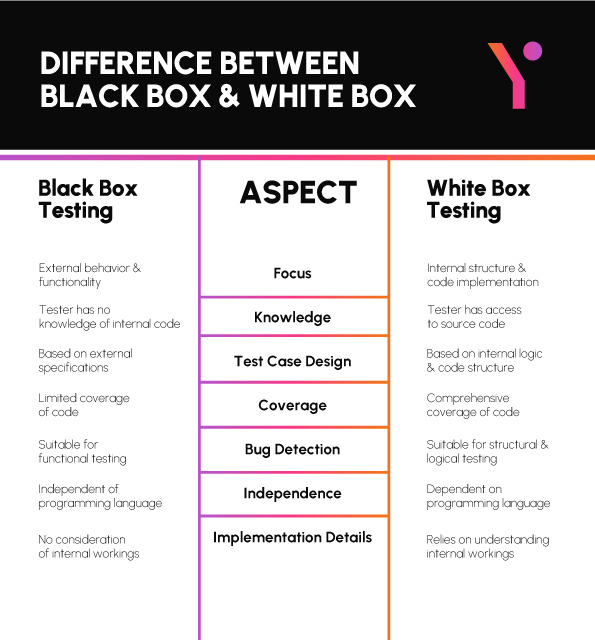
Difference between Black box vs White Box Testing
In software testing, two primary methodologies, black box testing and white box testing, offer distinct approaches but share the same objective: Upkeeping Applications flawlessly.
The table below outlines key difference between black box and white box testing across various aspects, highlighting their focus, level of knowledge required, test case design, coverage, bug detection capabilities, independence from programming language, and consideration of implementation details.
| Aspect | Black Box Testing | White Box Testing |
| Focus | External behavior and functionality | Internal structure and code implementation |
| Knowledge | Tester has no knowledge of internal code | Tester has access to source code |
| Test Case Design | Based on external specifications | Based on internal logic and code structure |
| Coverage | Limited coverage of code | Comprehensive coverage of code |
| Bug Detection | Suitable for functional testing | Suitable for structural and logical testing |
| Independence | Independent of programming language | Dependent on programming language |
| Implementation Details | No consideration of internal workings | Relies on understanding internal workings |
When to Use Each Software Testing Approach
Black Box Testing
- Use black box testing when the focus is on validating external behaviour and functionality without delving into internal code details.
- Ideal for testing software from an end-user perspective and validating functional requirements.
- Suitable for acceptance testing, usability testing, and system integration testing.
White Box Testing
- Choose white box testing when comprehensive coverage of code and internal structure testing is required.
- Appropriate for unit testing individual functions or modules, ensuring algorithmic correctness, and detecting complex bugs.
- Effective in identifying performance bottlenecks, security vulnerabilities, and code optimisation opportunities.
Combining Black Box vs White Box Testing for Comprehensive Quality Assurance
Combining black box and white box testing enables organisations to streamline software testing while ensuring comprehensive quality assurance throughout the software development lifecycle.
Since Black box testing validates software from an end-user perspective, focusing on functionality and usability.
On the contrary, White box testing provides deep insights into the internal structure and logic of the software, facilitating thorough code coverage and bug detection.
Integrating both approaches can achieve a balanced testing strategy that addresses both external behavior and internal implementation details, leading to robust and reliable software products.
Conclusion
We have found out the major difference between black box vs white box testing and pros and cons of both. While black box testing focuses solely on external behavior and functionality without delving into the internal code, white box testing provides an in-depth examination of the logic and entire internal structure of the software.
By grasping the difference between black box and white box testing, software development teams can tailor their testing strategies to suit project requirements and objectives effectively. Moreover, combining both Black box and White box testing methodologies can yield comprehensive quality assurance, addressing a wide spectrum of defects and issues.
Ultimately, in today’s fast-paced software development, everything depends on user satisfaction, and product reliability is non-negotiable; a balanced testing approach that incorporates both Black box and White box testing is indispensable. By embracing these methodologies and their exact differences, organisations can deliver software products of the highest caliber, meeting and exceeding user expectations in an ever-evolving market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Neither method is inherently “better”. The ideal approach depends on your project’s needs, resources, and risk tolerance. Most of the time, a more thorough covering comes from utilising both Black Box and White Box tests together.
Black box testing focuses solely on the functionality of a software application without assessing its internal coding and structure.On the other hand, white box testing is about examining the internal structure and logic of the software by inspecting its source code.In essence, black box testing tests from the outside, while white box testing tests from within the software’s code.
Black box testing offers independent testing, checks software from a user’s perspective, and is not dependent on programming languages.
Black box testing has limited coverage of code, making it difficult to identify certain types of bugs, and can struggle with determining the root causes of issues.
White box testing offers comprehensive coverage of code, enables early detection of integration issues, and facilitates code optimisation.
White box testing is tough because you have to access the source code, making it dependent on programming languages, and can be time-consuming due to detailed test case design.
Yes, combining black box and white box testing methodologies can provide comprehensive quality assurance by leveraging the strengths of both approaches.
There are numerous tools available, depending on the testing type. Examples include:Selenium for automated browser testingJUnit for unit testing in JavaSoapUI for web services testingLoadRunner for performance testingAppium for mobile app testing
Have questions or feedback?
Get in touch with us and we‘l get back to you and help as soon as we can!




